The rising cost of living in Asia & the US
The rising cost of living has been a significant challenge for individuals around the world. People have felt the brunt of this increase, particularly in everyday essentials like groceries, housing, and transport.
To better understand these issues, Rakuten Insight Global interviewed 6,500 adults 16+ years old from 13 proprietary panels across Asia & the US. The survey focused on areas of spending that have been most impacted by this increase in the cost of living, as well as what adaptations consumers are making to reduce their spending.
The cost of living crisis
The cost of living crisis is felt in all of our Asia & US panels, except for Japan which seems to have largely escaped the effects in the immediate aftermath of the pandemic.
Generally, the majority strongly agree that ‘The cost of living has increased since the covid pandemic’, with US respondents and those from Singapore and the Philippines leading this sentiment at 65% and 57%, respectively.
Interestingly, only 8% of Japanese respondents strongly agreed with the statement, compared to an average of 40% across all markets. In fact, 49% of Japanese respondents neither agreed nor disagreed with the statement. By far the highest, 14% of consumers in Japan either disagree or strongly disagree that the cost of living has increased compared to the 5% average overall.
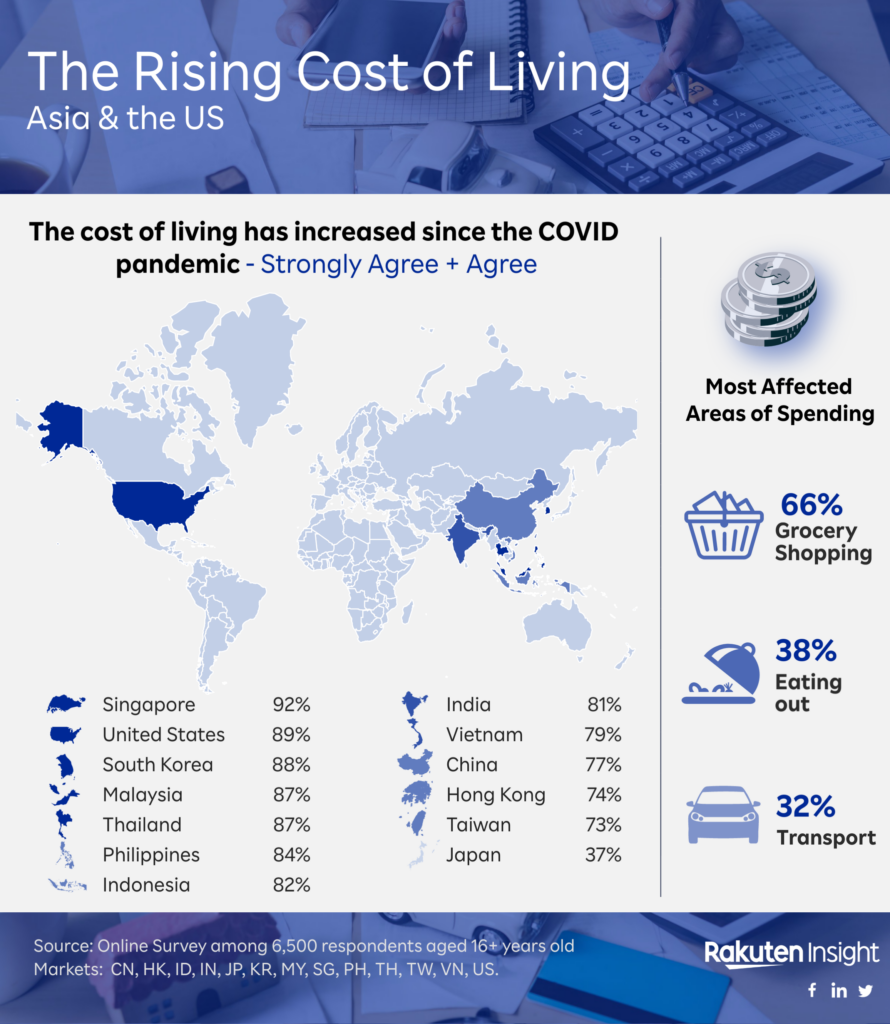
Most affected areas of spending
When it comes to the impact of the rising cost of living, it seems grocery shopping has taken the biggest hit with 66% of consumers reporting increased expenses. Eating out and transportation were next in line, both being chosen by over 30% of those surveyed.
Consumers in the Philippines and the US seemed to be most affected by grocery costs, with 84% and 82% of respondents, respectively, reporting this as a significant expense. On the other hand, Singapore had the highest number of people affected by eating out costs, with 63% reporting an increase in spending in this area. In Thailand, consumers are feeling the impact of increased fuel prices, with 54% choosing transport and 48% choosing housing as the most affected areas.
Reducing spending across markets
When it comes to reducing expenses, consumers are looking closely at two major areas: Eating Out and Travelling. In general, the average percentage of people considering cutting back on these expenses is around 51% and 32%, respectively. However, a closer look at the breakdown by market reveals some interesting differences.
For instance, Indian consumers are much less likely than the average to cut back on dining out, with only 37% saying they would reduce this expense, compared to 51%. This could be due to the abundance of cheap and tasty food options available in India. Similarly, Indian travellers are less likely to cut their spending on trips, with only 20% saying they would reduce this expense, compared to 32% overall. This could reflect the attractive domestic travel options available to Indian consumers at a lower price than international travel.
On the other hand, 49% of Japanese consumers said they would consider reducing travel expenses – possibly related to high profile exchange rate challenges of the yen compared to the US dollar.
Conclusion
The worldwide rise in the cost of living has changed the very nature of life for many individuals, forcing them to make difficult decisions when it comes to managing their finances. Grocery shopping emerged as a significant economic burden according to over two-thirds of those surveyed, with Eating Out coming in second at 38%.
Different markets have shown varying levels of resilience, with Japan seemingly escaping the brunt of the effects. At the same time, people in other nations have looked to reduce expenses in areas such as Eating Out (51%) and Travel (32%).
It is clear that the rising cost of living has created a challenging environment around the world, and people have to reconsider their spending habits to get by.
Download the full data here:
Related articles: 2022 Impact of COVID-19 on consumer behaviour
For more infographics, updates and our original survey reports, follow us on LinkedIn or subscribe to our newsletter at the bottom of the page.